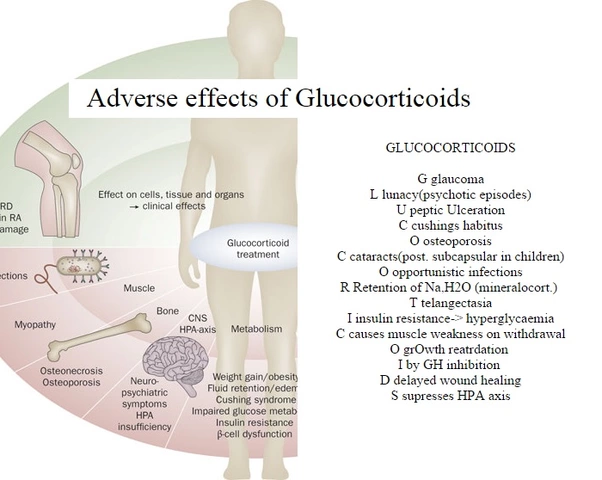
Calcium Acetate Side Effects – Quick Guide
Calcium acetate is used to lower phosphate levels in people with kidney disease. It works by binding phosphate in the gut so it can’t be absorbed. While it helps keep blood phosphate in check, many users notice side effects. Knowing which reactions are normal and which need a doctor’s eye can save you a lot of worry.
Common Symptoms
Most people report a mild, uncomfortable feeling in the stomach. Bloating, gas, and a feeling of fullness are the top complaints. You might also notice a chalky taste in your mouth or a dry cough that comes on after a dose. These reactions usually appear within the first few days of starting the medication and often fade as your body adjusts.
Another frequent issue is constipation. Calcium acetate adds extra calcium to your diet, and calcium can slow down bowel movements. If you’re prone to constipation, you may see fewer trips to the bathroom or harder stools. Drinking plenty of water and adding fiber‑rich foods can help keep things moving.
Some users develop a low‑grade fever or feel a bit shaky. This is less common but can happen if the pill irritates the lining of the stomach. If you notice a persistent fever, it’s a sign to talk to your pharmacist or doctor.
When to Call a Doctor
If any of these symptoms get worse after a week, or if you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or blood in the stool, stop the medication and seek medical help right away. These could be signs of a more serious reaction, like an ulcer or an allergic response.
Shortness of breath or a rapid heartbeat are red flags too. Although rare, calcium acetate can affect calcium levels in the blood, leading to high calcium (hypercalcemia). Symptoms of hypercalcemia include confusion, muscle weakness, and irregular heartbeats. If you feel any of these, call your doctor immediately.
Pregnant or nursing women should be extra cautious. Calcium acetate can cross the placenta, and the safety data is limited. Discuss any plans for pregnancy with your healthcare provider before starting or continuing the drug.
Finally, if you’re taking other medicines that also contain calcium or phosphate binders, talk to a pharmacist about possible interactions. Overlapping doses can raise calcium too high or cause an imbalance in electrolytes.
Bottom line: most side effects of calcium acetate are mild and go away on their own, but staying alert to serious signs helps you stay safe. Keep a simple log of what you feel after each dose – it makes the conversation with your doctor more productive.
Want to reduce side effects? Take the pill with meals, stay hydrated, and pair it with a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. If constipation is a problem, a daily probiotic or a small amount of magnesium can make a big difference.
Remember, the goal of calcium acetate is to protect your kidneys by controlling phosphate. When you manage the side effects well, you get the benefit without the hassle.
Calcium Acetate Drug Interactions: In‑Depth Review & Practical Guide
A comprehensive look at calcium acetate drug interactions, comparing it to other phosphate binders, with clear management tips and a handy FAQ.