Antifungal Treatment: Your Guide to Winning the Fungal Fight
When dealing with antifungal treatment, a medical approach that uses drugs to eliminate fungal pathogens and relieve related symptoms. Also known as fungal therapy, it can be applied on the skin, taken by mouth, or administered intravenously depending on the infection site. Antifungal treatment is essential because fungi like Candida or dermatophytes can cause anything from mild itching to serious systemic disease.
Key Players in Fungal Care
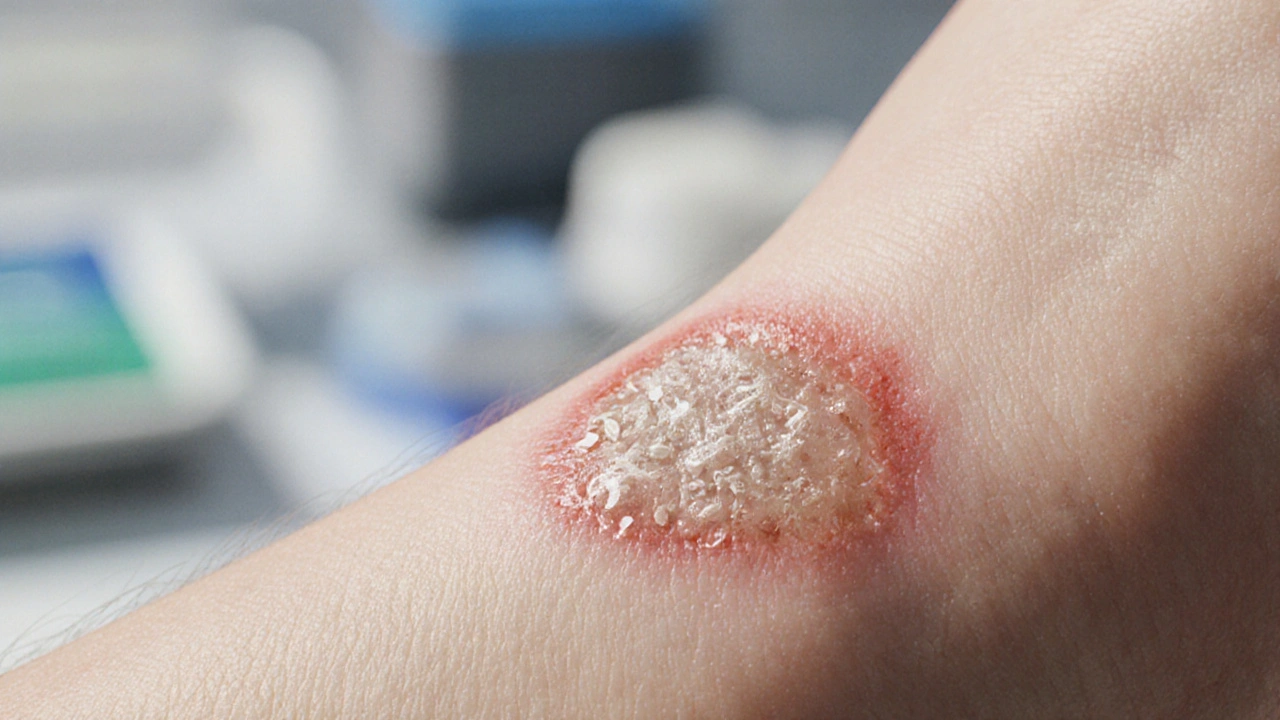
One of the most common foes is Candida infection, a yeast overgrowth that shows up as oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, or diaper rash. Recognizing Candida early helps you pick the right drug class and avoid unnecessary side effects. Another crucial element is topical antifungal, creams, powders or sprays applied directly to the skin or nails to treat superficial infections such as athlete's foot or ringworm. Topicals act fast, stay localized, and often avoid the systemic risks of pills.
When the infection has spread beyond the skin, oral antifungal, tablets or capsules like fluconazole and itraconazole that travel through the bloodstream become necessary. Oral agents reach deeper tissues, treat nail infections, and manage recurrent Candida in the gut or blood. However, they require careful dosing and monitoring because they can interact with other medications and affect liver function.
Choosing between topical and oral routes isn’t just about convenience; it reflects a semantic triple: antifungal treatment encompasses both topical and oral agents. A proper diagnosis requires laboratory confirmation, and the selected therapy must match the fungal species and infection severity. Ignoring these connections can lead to treatment failure or promote drug‑resistant strains.
Resistance is a growing concern. Overusing over‑the‑counter creams or skipping prescribed courses gives fungi a chance to adapt. Studies show that repeated exposure to azole‑based creams can select for resistant Candida, making later infections harder to clear. To combat this, clinicians advise finishing the full regimen, even if symptoms improve early, and rotating drug classes when multiple infections occur.
Safety matters too. Topical agents can cause skin irritation or allergic reactions, while oral drugs may cause nausea, headache, or liver enzyme changes. Always check for drug interactions—especially with cholesterol meds, anticoagulants, or certain antibiotics. If you have underlying liver disease, kidney issues, or are pregnant, your doctor may favor a topical option or adjust the oral dose.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into each of these topics. Whether you’re looking for a step‑by‑step dosage guide, a side‑effect checklist, or tips on buying reputable generic antifungals online, our collection covers the full spectrum of fungal care. Keep reading to equip yourself with the knowledge you need to pick the right antifungal strategy for your situation.
How Fungal Infections Affect Wound Healing & Prevention Strategies
Explore how fungal infections impact wound healing, key pathogens, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips to speed recovery and avoid chronic wounds.